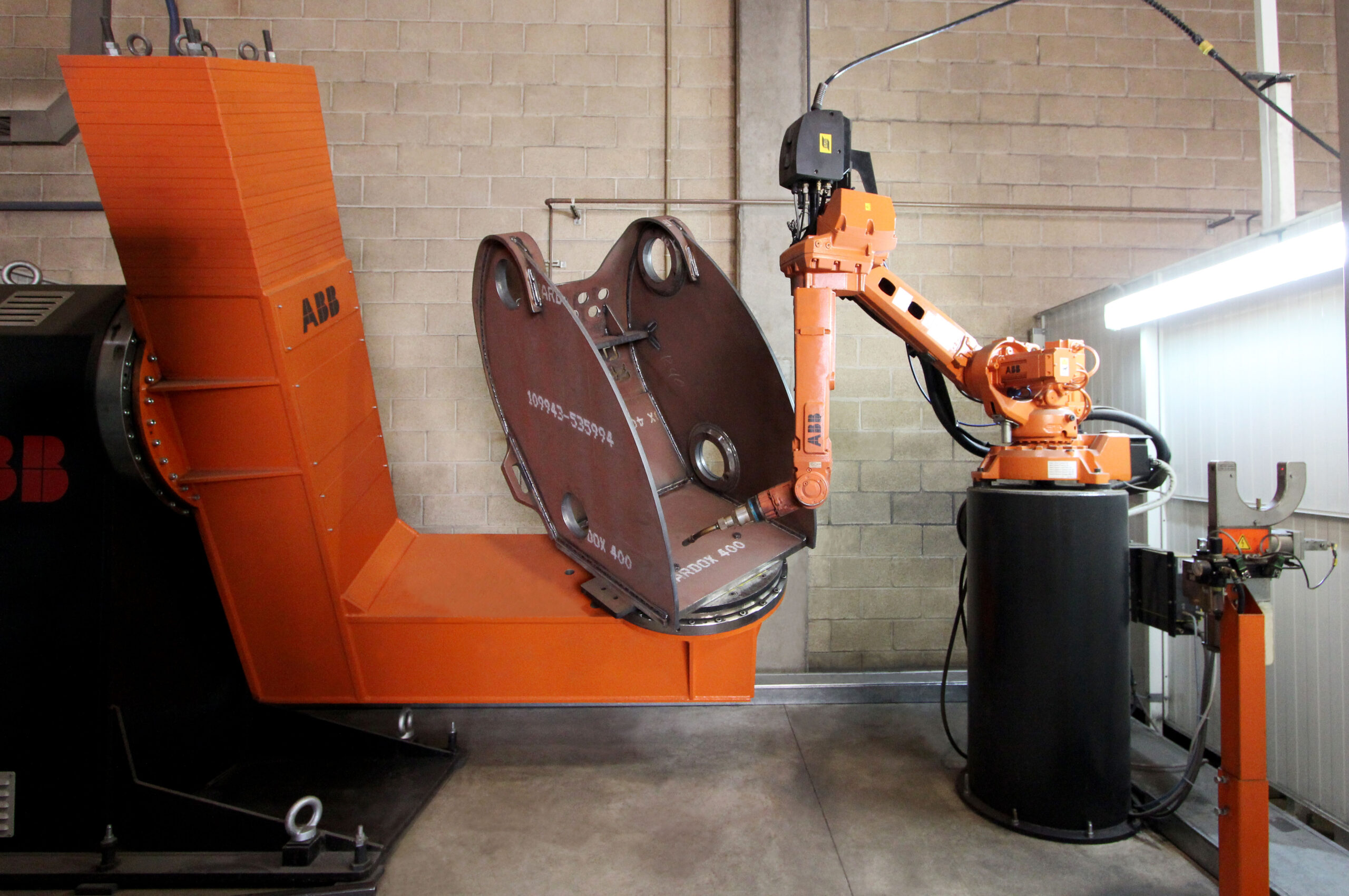
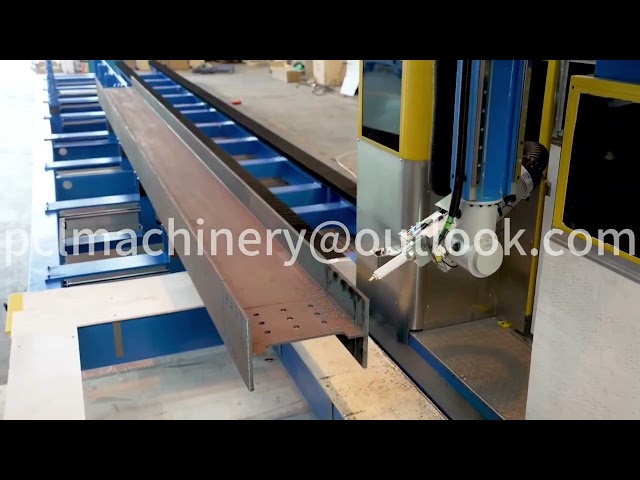
The application of industrial robots in the field of welding is referred to as welding robots. These are industrial robots engaged in welding processes and mainly consist of two parts: the robot itself and specialized welding equipment. The robot consists of the robot body and the control cabinet (hardware and software), while the welding equipment, taking arc welding and spot welding as examples, consists of the welding power supply (including its control system), wire feeder (for arc welding), welding gun (or clamp), and other components. For intelligent robots, a sensing system, such as a laser or vision sensor and its control devices, should also be included.
1. Characteristics of Arc Welding Robots
Arc welding robots commonly use gas-shielded welding methods (MAG, MIG, TIG). The common welding power supplies, including thyristor-based, inverter-based, waveform control, and pulsed or non-pulsed types, can all be integrated with the robot for arc welding. Since the robot control cabinet uses digital control, and most welding power supplies use analog control, an interface needs to be added between the welding power supply and the control cabinet.
In recent years, many robot manufacturers, both domestic and international, have developed specific supporting welding equipment, which already has the appropriate interface boards installed, meaning that there is no need for an additional interface box in the arc welding robot system. For example, the Shanghai Fraus FRB050 stainless steel automation welding robot set is customized with a digital pulse welder developed by Beijing Times Technology, achieving perfect welding of 1 cm small round welds, surpassing the four major family brands. As the use of stainless steel welding and aluminum welding becomes more widespread, both domestic and international welding equipment is moving toward the development of digital welding machines. It should be noted that during the arc welding robot’s work cycle, the arc time accounts for a large proportion. Therefore, when selecting the welding power supply, its capacity is generally determined based on a 100% duty cycle.
The wire feeding mechanism can be installed on the robot’s upper arm or placed outside the robot. In the former case, the hose between the welding gun and the wire feeder is shorter, which helps maintain wire feeding stability. In the latter case, the hose is longer, and when the robot positions the welding gun at certain locations, causing the hose to bend excessively, it can significantly affect the stability of wire feeding. Therefore, the installation of the wire feeder must consider ensuring the stability of the feeding process.
2. Characteristics of Spot Welding Robots
Spot welding robots use integrated welding pliers, with the welding transformer mounted behind the pliers. Therefore, the transformer for spot welding robots must be as compact as possible. For smaller transformers, a 50Hz AC power supply is used, while for larger transformers, industrial applications are increasingly adopting inverter technology to convert 50Hz AC into 600-700Hz AC, reducing the size and weight of the transformer. After conversion, the 600-700Hz AC can be used directly for welding or further rectified for DC welding, with welding parameters adjusted by a timer. Currently, new timers have been digitized, so the robot control cabinet can directly control the timer without the need for an additional interface.
The welding pliers of spot welding robots are driven by electric servo motors, with the opening and closing of the pliers controlled by the servo motor and feedback from a coder. This allows the opening of the pliers to be set as needed and adjusted continuously, and the pressing force between the electrodes can also be adjusted without steps.
Advantages of electric servo spot welding pliers include:
- (1) The welding cycle for each weld point can be greatly reduced because the opening of the pliers is precisely controlled by the robot, enabling the pliers to begin closing during the robot’s movement between weld points. After finishing one weld, the pliers open while the robot moves, avoiding unnecessary delays.
- (2) The opening degree of the pliers can be adjusted based on the workpiece, and the opening degree can be minimized to save time during the opening and closing process.
- (3) The pressure during closing is adjustable, and when closing, the electrodes press gently to reduce impact deformation and noise.
3. Problems in Welding Robot Applications and Solutions
- Welding Offset Issue: This may occur due to incorrect welding position or issues with the welding gun’s search process. The TCP (Tool Center Point) of the welding gun should be checked and adjusted. If this occurs frequently, it may be necessary to check the zero position of the robot’s axes and re-calibrate them.
- Edge Burnthrough: This can be caused by improper welding parameters, incorrect welding gun angle, or positioning. Adjustments can be made accordingly.
- Porosity Issue: This can occur due to insufficient gas protection, excessive primer thickness on the workpiece, or insufficiently dry protective gas. These can be resolved by making the appropriate adjustments.
- Excessive Spatter: This may result from improper welding parameters, gas composition issues, or the excessive protrusion of the welding wire. The machine’s power can be adjusted to modify the welding parameters, and the gas mixture ratio can be adjusted to control spatter.
- Arc Pits at Weld End: This can be addressed by programming a buried arc pit function to fill it during the work cycle.
4. Common Failures in Robot Welding Systems
- Gun Collision: This may be due to assembly deviations of the workpiece or inaccurate TCP of the welding gun. Check the assembly and correct the welding gun TCP.
- Arc Fault (Unable to Strike Arc): This can occur if the welding wire does not contact the workpiece or the process parameters are too low. Try manually feeding the wire, adjusting the distance between the welding gun and the weld, or adjusting the process parameters.
- Protective Gas Monitoring Alarm: This could indicate a problem with the cooling water or protective gas supply. Check the cooling water and protective gas pipes for issues.
5. Programming Skills for Welding Robots
- (1) Choose a reasonable welding sequence to reduce welding deformation and minimize the welding gun’s path length.
- (2) The transition of the welding gun in space should have a short, smooth, and safe trajectory.
- (3) Optimize welding parameters by creating test workpieces for welding experiments and process evaluation to determine the best parameters.
- (4) Use a reasonable position for the positioner, welding gun posture, and relative position of the welding gun to the joint. After the workpiece is fixed on the positioner, if the weld is not in an ideal position or angle, adjust the positioner during programming so that the welding seams achieve a horizontal position sequentially. The welding gun’s relative position to the joint should be carefully observed during programming, which requires skill and experience.
- (5) Insert cleaning programs at appropriate points. After writing a certain length of welding program, insert a cleaning program to prevent spatter from blocking the welding nozzle and ensure the welding gun remains clean, improving nozzle life and ensuring reliable arc starting.
- (6) The program should be tested and adjusted repeatedly during the welding process to form an optimal program.
Conclusion
With the development of advanced manufacturing technologies, automation, flexibility, and intelligence in welding product manufacturing have become inevitable trends. Today, robotic welding has become a major symbol of modern welding automation technology, especially as demand for stainless steel and aluminum welding increases. Due to their versatility and reliability, welding robots are gaining increasing attention.