Technical Study on MAG Welding of Steel Structures by Welding Robots
Abstract
Metal Active Gas (MAG) welding, utilizing a consumable wire electrode and a shielding gas mixture, is widely employed in robotic welding systems for steel structures due to its high efficiency, adaptability, and cost-effectiveness. This study explores the application of welding robots in MAG welding of steel structures, focusing on process parameters, robotic system integration, and quality control. Key challenges, such as weld imperfection mitigation and automation optimization, are addressed, with an emphasis on achieving high-quality welds in industrial applications.
Introduction
Welding robots have revolutionized the fabrication of steel structures, offering precision, repeatability, and productivity unmatched by manual methods. MAG welding, a subset of Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), uses a shielding gas typically composed of argon and carbon dioxide to protect the weld pool from atmospheric contamination. Its versatility makes it ideal for welding steel components in industries such as automotive, construction, and heavy machinery. This paper examines the technical aspects of MAG welding using robotic systems, highlighting advancements, challenges, and solutions for welding steel structures.
MAG Welding Process
MAG welding involves a continuous wire electrode fed through a welding gun, with an electric arc forming between the wire and the workpiece. The shielding gas, typically a mixture of 80% argon and 20% CO2, prevents oxidation and ensures stable arc characteristics. Key parameters influencing weld quality include:
- Current and Voltage: Typically, 150–300 A and 20–30 V for steel structures, depending on material thickness.
- Wire Feed Speed: Ranges from 4 to 12 m/min, directly affecting deposition rate.
- Travel Speed: Optimized between 0.3–0.8 m/min to balance penetration and bead formation.
- Shielding Gas Flow: 10–20 L/min to ensure adequate coverage without turbulence.
Robotic systems precisely control these parameters, enabling consistent welds across complex geometries.
Robotic Welding Systems
Modern welding robots, such as those from FANUC, ABB, or KUKA, integrate advanced sensors, control systems, and programming interfaces. Key components include:
- Manipulator: A 6-axis robotic arm for precise torch positioning.
- Welding Power Source: Inverter-based systems for stable arc control.
- Sensors: Laser seam tracking and vision systems to adapt to joint variations.
- Programming: Offline programming software (e.g., RoboDK) and teach pendants for path planning.
These systems enable high-speed welding with minimal human intervention, improving productivity and safety.
Advantages of Robotic MAG Welding
- Consistency: Robots maintain uniform weld quality, reducing defects like porosity or incomplete fusion.
- Productivity: High deposition rates and continuous operation increase throughput.
- Flexibility: Robots adapt to various joint configurations and material thicknesses.
- Safety: Automation reduces worker exposure to hazardous fumes and arc radiation.
Challenges in Robotic MAG Welding
Despite its advantages, robotic MAG welding faces several challenges:
- Weld Imperfections: Issues like spatter, undercut, or lack of penetration arise from improper parameter settings or joint misalignment.
- Material Variability: Steel structures often vary in composition and thickness, requiring adaptive control systems.
- Programming Complexity: Complex geometries demand sophisticated path planning and collision avoidance.
- Cost: Initial investment in robotic systems and maintenance can be significant.
Solutions and Innovations
Recent advancements address these challenges effectively:
- Adaptive Control: Real-time monitoring using laser sensors adjusts parameters to account for joint gaps or misalignments.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI algorithms optimize welding parameters based on material properties and joint geometry, reducing defects.
- Seam Tracking: Vision-based systems ensure accurate torch positioning, even on irregular surfaces.
- Hybrid Welding: Combining MAG with laser welding enhances penetration and reduces heat input, improving weld quality for thick steel plates.
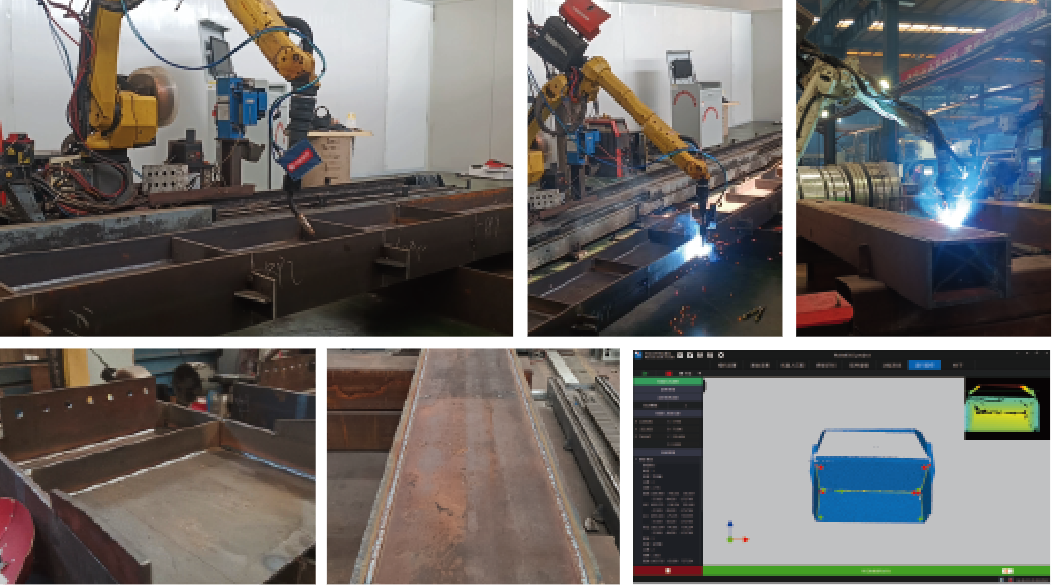
Quality Control
Ensuring weld quality is critical for structural integrity. Non-destructive testing (NDT) methods, such as ultrasonic testing and X-ray inspection, detect internal defects. Robotic systems integrate inline quality monitoring, using sensors to measure weld bead geometry and detect anomalies. Statistical process control (SPC) analyzes data to maintain consistency across production runs.
Case Study: Automotive Industry
In automotive manufacturing, robotic MAG welding is used to join steel chassis components. A typical setup involves a 6-axis robot with a 250 A power source welding 2–5 mm thick steel sheets. Parameters include a wire feed speed of 8 m/min, 25 V, and a travel speed of 0.5 m/min. Laser seam tracking ensures precise joint following, achieving a defect rate below 1%. This setup increased production efficiency by 30% compared to manual welding.
Future Trends
The future of robotic MAG welding lies in further automation and intelligence:
- Industry 4.0 Integration: IoT-enabled robots share data for predictive maintenance and process optimization.
- Collaborative Robots: Cobots work alongside human welders for flexible production lines.
- Sustainability: Low-energy power sources and optimized gas mixtures reduce environmental impact.
Conclusion
Robotic MAG welding of steel structures offers significant advantages in precision, productivity, and safety. By addressing challenges through adaptive control, AI, and advanced sensors, manufacturers can achieve high-quality welds with minimal defects. As technology evolves, robotic welding systems will continue to drive efficiency and innovation in steel fabrication.