The development of industrial robots can be traced back to the 1950s. With technological advancements and industrialization, the demand for increased production efficiency and reduced labor costs has become more urgent, driving the research and application of industrial robots. Industrial robots can replace human labor in hazardous environments involving high temperatures, high pressure, toxic substances, and other adverse conditions. They can complete a large volume of repetitive, high-precision tasks within a short time without suffering from fatigue or human errors. The advancement of industrial robots enhances corporate competitiveness and innovation, promotes industrial upgrades and technological progress, and drives traditional industries toward intelligence and automation.
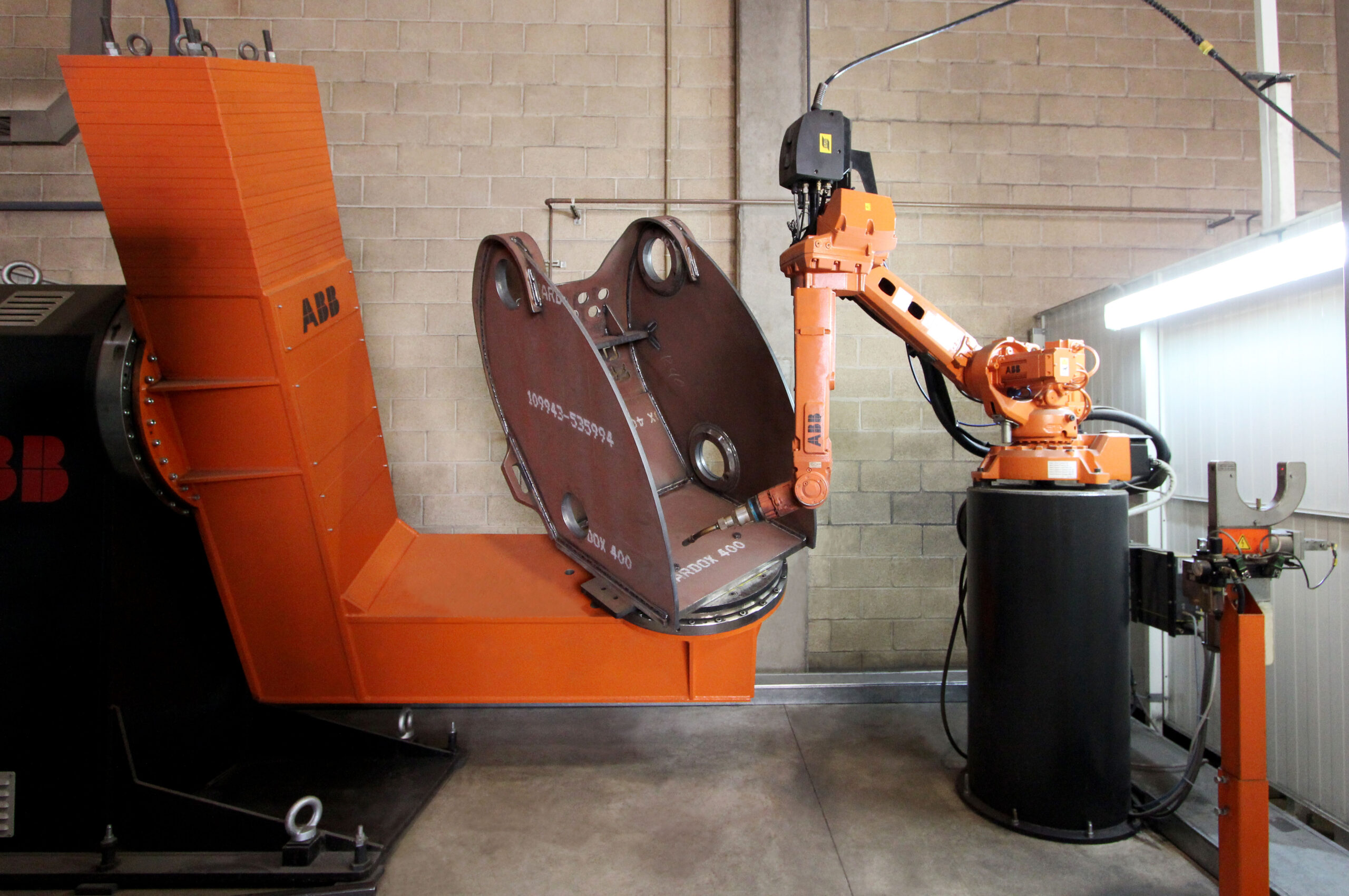
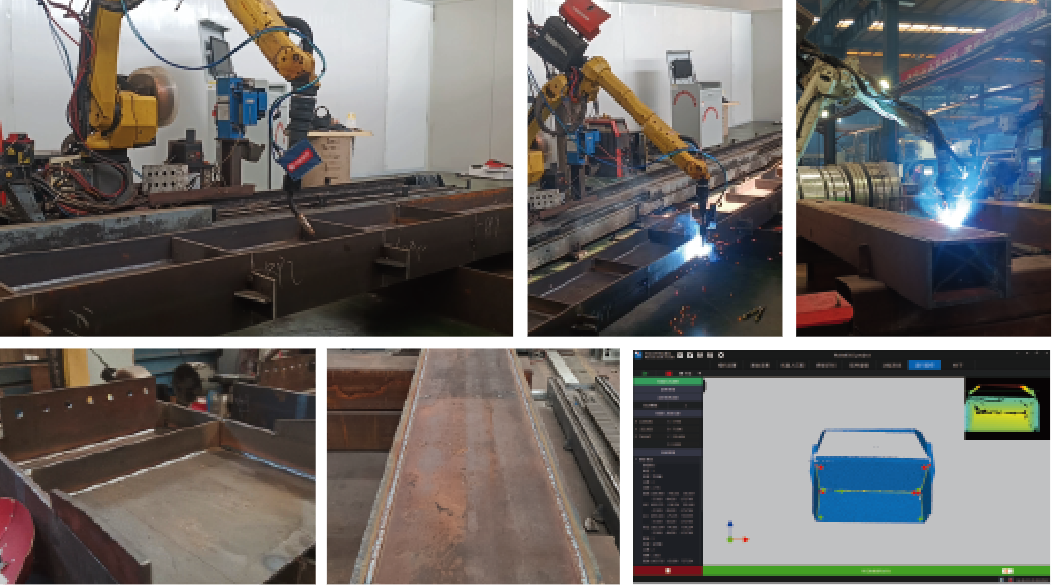
Welding occupies a crucial position in modern manufacturing. Traditional manual welding methods involve harsh working conditions, high labor intensity, and require skilled operators, which can pose potential health hazards. The adoption of industrial robots for intelligent welding transforms the rigid automation welding model, enabling flexible and intelligent automation for small-batch, single-piece welding production. This revolutionary advancement in welding intelligence results in more stable welding quality, significantly improved working conditions, and enhanced labor productivity. Robotic intelligent welding is widely used in industries such as automobile manufacturing, metal structure construction, general machinery manufacturing, military weapon production, engineering machinery manufacturing, and aerospace. It is particularly beneficial in mass production and hazardous work environments, where welding processes, equipment, and technologies have become increasingly sophisticated.
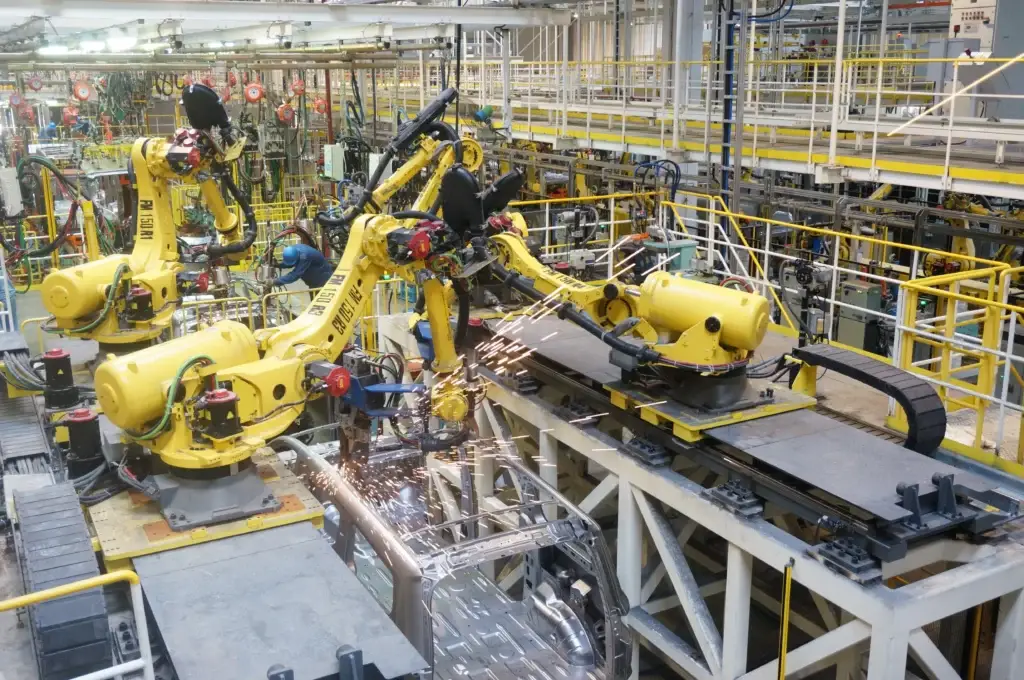

1 Overview of Industrial Robot Applications
Industrial robots are intelligent devices that integrate human-like operations, automatic control, programmability, and the ability to execute tasks in three-dimensional space. They consist of manipulators, controllers, servo drive systems, and sensors, enabling them to assist humans in performing monotonous, heavy, and repetitive tasks. Their adaptability allows them to function efficiently in harsh external environments without constraints. With continuous technological advancements, industrial robotics are being increasingly adopted across various industries, particularly in manufacturing.
In fields where chemical materials pose health risks, such as handling, palletizing, and spraying, industrial robots prevent potential harm to human workers. Approximately 40% of the world’s industrial robots are used in automobile manufacturing, making robotic technology the foundation for modernizing and automating the automotive industry.
Common types of industrial robots in intelligent manufacturing include inspection robots, welding robots, handling robots, spraying robots, and grinding robots. Inspection robots measure part dimensions, identify colors and shapes, and replace manual inspections to ensure product quality. Welding robots, the most widely used, are primarily employed for welding automotive body structures and are indispensable automation equipment in the automotive industry. Handling robots are used for material transportation, palletizing, and loading/unloading, significantly reducing manual labor efforts.
With the integration of emerging technologies such as cloud computing, big data, IoT, AI, augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), 3D printing, additive manufacturing, and digital twins, industrial robotics has matured significantly. Automation and intelligence levels continue to improve, enhancing system performance and expanding the application space of industrial robots.
2 Intelligent Welding Technology
Intelligent welding technology utilizes computers to mimic and enhance human perception, learning, decision-making, and monitoring capabilities, forming an intelligent information system that integrates human expertise with advanced physical systems. It plays an increasingly vital role in modern manufacturing by combining AI, machine learning, and automation to improve and optimize welding processes.
2.1 Sensing Technology
Sensing technology is crucial in intelligent welding, as sensors collect real-time welding data such as temperature, voltage, current, and speed. These data enable real-time adjustments to welding parameters, ensuring weld quality and stability.
2.2 Machine Vision Technology
Machine vision technology aids in detecting and identifying weld seams using cameras and image processing algorithms. It enables precise weld path planning and seam tracking, improving welding accuracy and efficiency.
2.3 Control Algorithms
Control algorithms are key to intelligent welding, allowing real-time parameter adjustments based on sensor data. Common control algorithms include PID control, fuzzy control, and neural network control, which optimize welding operations.
2.4 Artificial Intelligence Technology
AI, including deep learning and reinforcement learning, enhances welding systems by learning from vast data sets to optimize parameters and improve welding quality and efficiency. AI also enables intelligent decision-making and adaptive control for welding processes.
2.5 Cloud Computing and IoT
Cloud computing and IoT facilitate remote monitoring, data sharing, and real-time welding process control by connecting welding equipment to cloud platforms. IoT enhances data exchange and collaboration among welding systems, improving production efficiency and flexibility.
2.6 Adaptive Control Technology
Adaptive control technology adjusts welding parameters in real-time based on workpiece material, shape, and welding conditions, improving system stability and ensuring consistent weld quality.
2.7 Intelligent Path Planning Technology
Intelligent path planning optimizes welding routes, minimizing time and energy consumption. This technology considers workpiece shape and welding angles to enhance efficiency and precision.
2.8 Data Analysis and Predictive Technology
Data analysis and predictive technology identify potential welding issues before they occur, reducing defect rates and optimizing welding processes through historical and real-time data analysis.
2.9 Virtual Reality Technology
VR technology simulates welding processes for design validation and operator training, reducing trial-and-error costs and improving workforce skills.
3 Specific Applications of Industrial Robots in Intelligent Welding

3.1 Multi-Robot Welding Systems
Traditional single-robot welding workstations no longer meet the needs of small-batch, flexible intelligent production. Multi-robot systems enhance task complexity, intelligent operation, and system flexibility. Studies have demonstrated that dual-robot welding systems can produce high-quality diesel engine frames with strong adaptability, stable quality, and high efficiency, particularly in shipbuilding applications
3.2 Offline Programming and Simulation
Offline programming methods reduce robot teaching time while improving welding seam formation. Research on shipbuilding V-groove butt joint multi-pass welding has led to innovative multi-pass welding methods that significantly enhance efficiency.
3.3 Intelligent Welding in Aerospace Equipment
Robotic welding systems have been successfully applied in aerospace equipment manufacturing, improving accuracy and efficiency. Advances include the development of 11-axis linkage variable polarity plasma arc welding equipment for complex aerospace components, enabling precise automated welding of spacecraft components.
4 Future Trends of Industrial Robots in Intelligent Welding
With ongoing technological advancements, industrial robots will achieve greater automation in welding, including automatic recognition of welding positions, parameter adjustments, and operations with minimal human intervention. Future robots will offer enhanced precision, flexibility, and adaptability to various welding tasks, supporting different welding methods like gas shielded welding, arc welding, and laser friction welding. Human-robot collaboration will also improve, integrating vision sensors for better real-time adjustments.
AI-powered robots will process and analyze welding data for optimized parameter settings, continuously learning and adapting to enhance performance. Expanding their application fields, these robots will further increase efficiency, quality, and intelligence in welding.
5 Conclusion
Industrial robots have vast potential in welding, improving efficiency, reducing labor costs, and ensuring high-quality, consistent welds. Their role in automation enhances production speed and precision. Future research should focus on refining robot accuracy and stability, developing advanced welding materials, and enhancing human-robot collaboration. Additionally, ensuring the safety and reliability of robotic systems in industrial environments remains a crucial area of study.