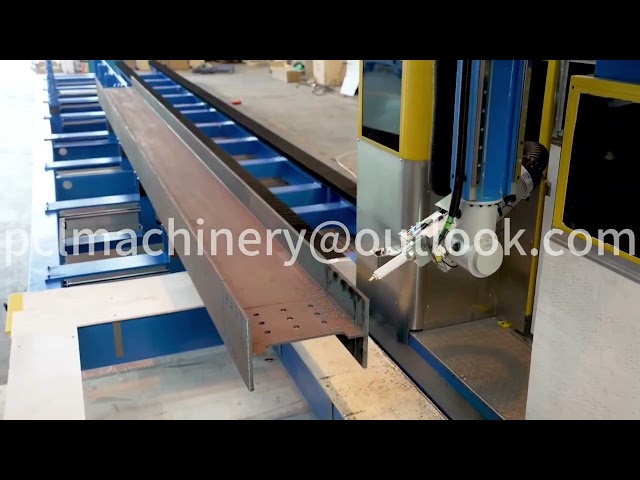
With the continuous advancement of technology, the automotive industry has increasingly high requirements for product quality. Laser cutting machines, with their advantages of fast cutting speed, high precision, narrow kerf, and wide cutting range, are widely used in automotive parts processing
As technology continues to advance, the automotive industry’s demands for product quality are rising. Laser cutting machines, with their characteristics of fast cutting speed, high precision, narrow kerf, and wide cutting range, are widely utilized in automotive component processing. This article mainly introduces the key factors affecting laser cutting quality and their control methods.
Laser cutting uses the energy of a laser beam to thermally cut materials, and molten metal is blown away with the help of auxiliary gas to form a kerf. During laser cutting, the laser serves as a light source, and the beam is guided through mirrors and focused by lenses. The focused beam is then directed at the material with high power density. The material absorbs the light energy and converts it into heat, causing it to melt and vaporize. The laser beam penetrates the material, and continuous kerfing is achieved as the beam moves at a constant speed.
Many factors influence the quality of laser cutting. This article discusses the effects of raw materials, programming, parameter control during the process, and external temperature on cutting quality based on practical work experience.
Raw Materials
The condition of raw materials directly affects laser cutting quality, as the surface state impacts the absorption of the laser beam. Surface roughness and oxidation layers can significantly alter surface absorption rates. Severely rusted or oily raw materials not only reduce cutting speed but may also cause blowholes or incomplete cuts, resulting in rough or excessively lumpy cut surfaces. Therefore, the material surface must be free of significant rust or oil stains before laser cutting. Severely rusted or oily parts should be returned to the supplier or storage; lightly rusted or oily parts may be polished or cleaned by operators.
Programming
Optimized cutting paths can improve cutting speed and ensure product quality. Laser cutting programs are created using specialized software, such as PM-300 and PM-200, with the latter being commonly used at our facility. Due to limitations of automatic programming software imposed by machine structure and part shapes, generated cutting programs may have drawbacks. For instance, parts that cross multiples of the machine’s spindle movement range may exhibit noticeable kerf marks or excessive lumps at connection points, affecting the parts’ appearance.
To address this, technicians must adjust programming software parameters, optimizing machine and subprogram parameters based on specific part characteristics. This ensures an optimal cutting path, avoids kerf overlaps at spindle multiples, and enhances product appearance.
Focal Point Position
The focal point position directly affects the cut’s cross-sectional state. Depending on the material, it can be set to zero focal length, negative focal length, or positive focal length. Optimal positioning minimizes kerf width and maximizes efficiency. Generally, the focal point should be on or slightly below the surface. For thick plates (e.g., 5–8 mm), positive focal length is used (see Figure 1), where the focal point is approximately 1.5 mm above the workpiece surface.
Cutting Nozzle
The cutting nozzle prevents molten debris from contaminating the focusing lens and controls gas flow for quality cutting. The distance between the nozzle and the workpiece affects the coupling of the gas flow with the kerf. Too close a distance increases back pressure, negatively impacting cutting quality, while too far results in energy loss. The optimal distance is 1–2 mm. Modern systems use capacitive sensors to maintain the set height. Nozzle deformation or contamination affects coaxial alignment with the laser beam, reducing cutting quality, particularly for thicker plates.
Cutting Speed
Cutting speed is inversely proportional to material density and thickness. Proper speed ensures smooth kerf lines and a clean cross-section without excessive molten debris. Too fast a speed results in incomplete cuts, rough cross-sections, and excessive slag (see Figure 3). Too slow a speed leads to wide kerfs, melting, or overburning at sharp angles. Observing spark patterns during cutting helps gauge speed: evenly spreading sparks indicate proper speed, while tilted sparks indicate excess speed, and clustered sparks indicate insufficient speed.
Auxiliary Gas
Auxiliary gas aids in blowing molten debris out of the kerf. Gas type depends on the material, e.g., oxygen for carbon steel, air for non-metals, and nitrogen for stainless steel. High-purity gas ensures better quality, with purity levels of 99.996% used at our facility. Incorrect gas pressure, however, may lead to poor quality, such as rough kerfs or incomplete cuts
Laser Power
Laser power is critical to cutting quality. Appropriate power results in smooth surfaces with no slag. Insufficient power causes incomplete cuts or excessive slag, while excessive power leads to melting
External Temperature
External temperature affects cutting quality, especially in summer. High ambient temperatures (32–33°C) reduce cooling efficiency, leading to lower energy output. Ensuring proper cooling and ventilation of mirrors, lasers, and compressors mitigates these issues. Our facility has added a cold dryer system for summer operations.
Conclusion
To ensure cutting quality, one must use qualified materials, optimized cutting paths, and appropriate parameters. As laser technology matures, its applications in the automotive and manufacturing industries will continue to expand.