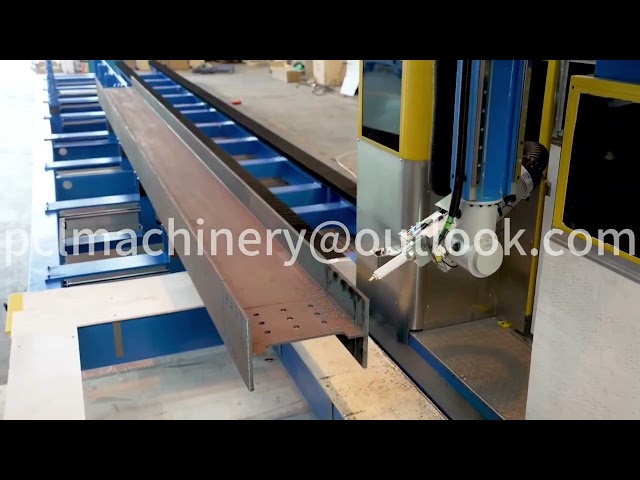
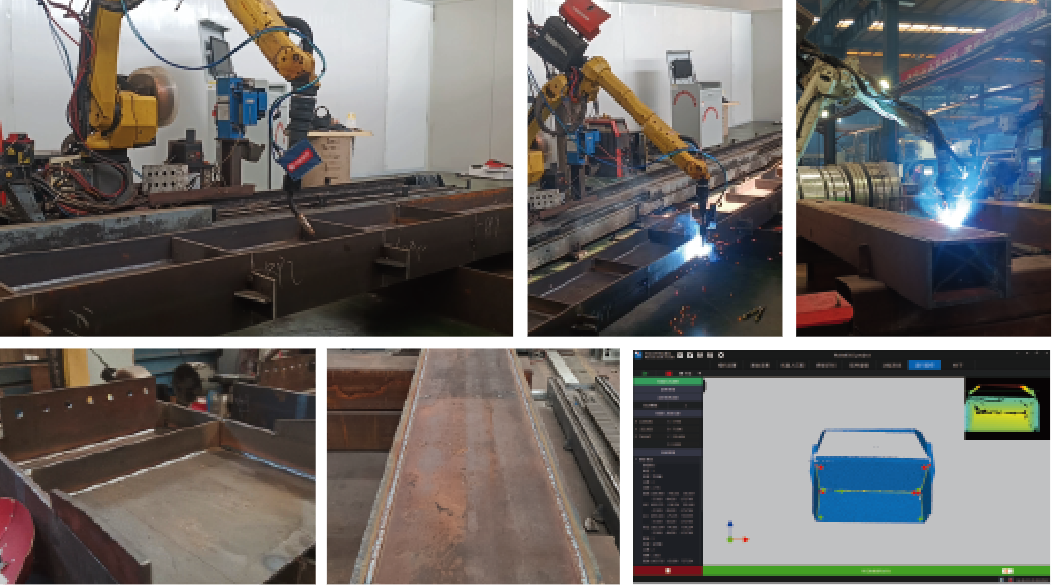
In modern manufacturing, robotic welding has revolutionized production lines by enhancing efficiency, precision, and safety. Among the advancements in this field, drag teaching robots welding stands out as a user-friendly method that simplifies programming. This article explores drag teaching robots welding, compares it with traditional robotic welding, and highlights its benefits, applications, and extended keywords like automated welding systems, robotic welders, and weld automation.
What is Drag Teaching Robots Welding?
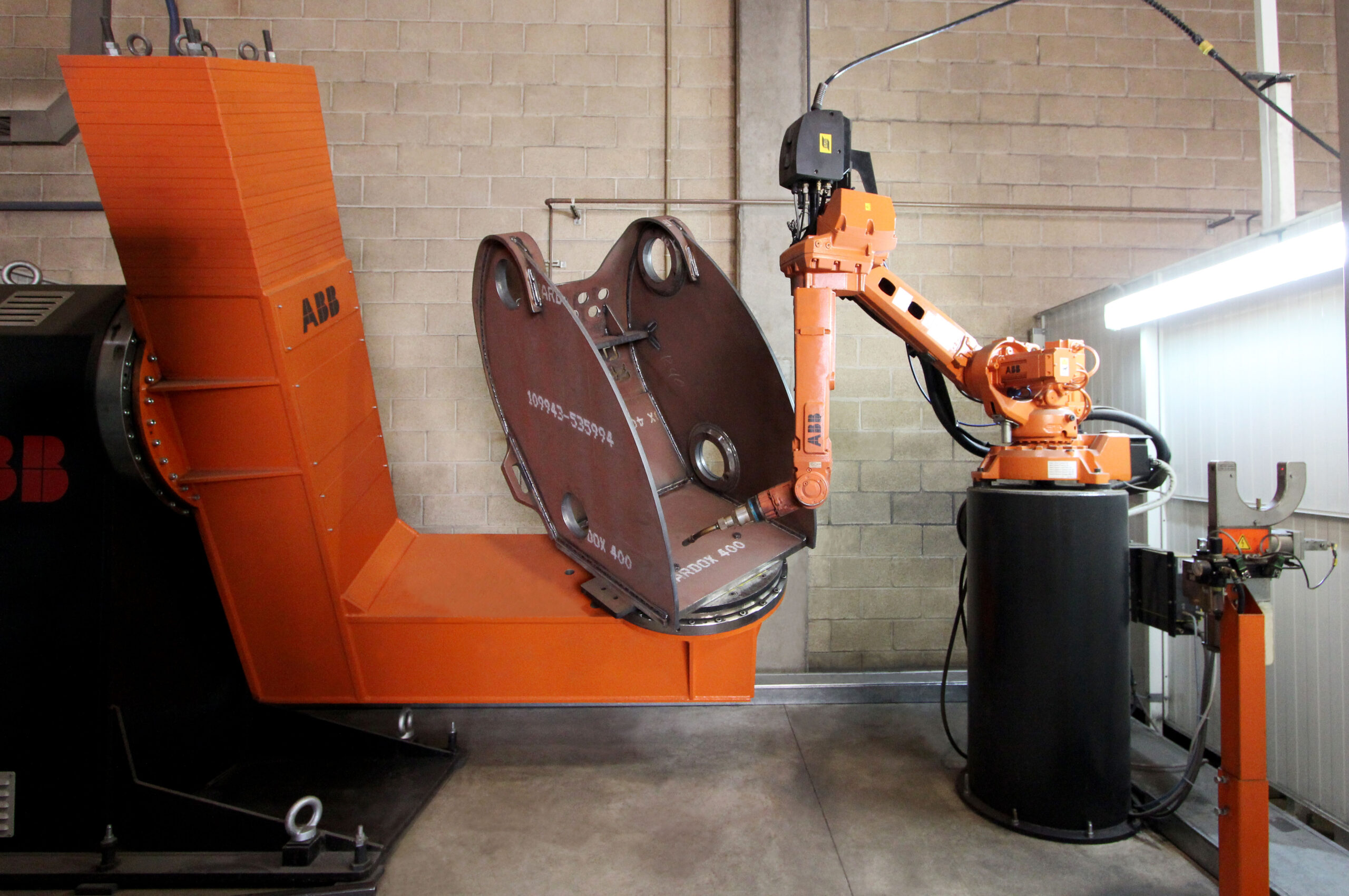
Drag teaching robots welding is an innovative approach where operators physically guide a robotic arm to teach it welding paths. Unlike traditional robotic welding, which relies on complex programming or offline simulation, drag teaching allows users to manually move the robot to desired positions, recording the trajectory for replication. This method reduces setup time and eliminates the need for advanced coding skills, making it ideal for small-to-medium enterprises (SMEs) and dynamic production environments.
Key features of drag teaching include:
Intuitive Operation: Operators with minimal training can program robots by dragging them along weld seams.
Flexibility: Easily adaptable to complex or irregular weld patterns, such as those in custom fabrication.
Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces programming costs and downtime, enhancing ROI for automated welding systems.
Traditional Robotic Welding: An Overview
Traditional robotic welding involves programming robots using software or teach pendants to execute precise welds. Commonly used in high-volume industries like automotive and aerospace, it excels in repetitive tasks requiring high accuracy. However, it has limitations, including lengthy setup times and the need for skilled programmers.
Key aspects of traditional robotic welding:
High Precision: Ideal for consistent, high-speed welds in mass production.
Complex Programming: Requires expertise in software like CAD/CAM or proprietary robot interfaces.
Scalability: Suited for large-scale operations with standardized weld requirements.
Comparing Drag Teaching Robots Welding and Traditional Robotic Welding
1. Programming Ease
Drag teaching robots welding is significantly easier to program. Operators guide the robot arm manually, recording weld paths in real-time. This contrasts with traditional robotic welding, where programmers input coordinates or use simulation software, often requiring days for complex tasks. For SMEs adopting weld automation, drag teaching reduces training costs and accelerates deployment.
2. Flexibility and Adaptability
Drag teaching excels in flexibility, allowing quick adjustments for small-batch or custom welds. For example, in shipbuilding or artistic metalwork, where weld patterns vary, drag teaching robots adapt seamlessly. Traditional robotic welders, while precise, struggle with frequent reprogramming, making them less suited for dynamic workflows.
3. Cost and ROI
Drag teaching robots lower initial costs by minimizing programming expenses and training needs. They also reduce downtime, as operators can reprogram robots on the fly. Traditional robotic welding systems, though efficient for high-volume production, involve higher upfront costs for software, training, and maintenance. For businesses exploring automated welding systems, drag teaching offers a faster ROI.
4. Precision and Consistency
Both methods deliver high precision, but traditional robotic welding slightly edges out in ultra-consistent, high-speed applications like automotive assembly. Drag teaching robots, while precise, may introduce minor variations due to manual input. However, advancements in sensor technology and feedback systems are closing this gap, making drag teaching viable for most welding tasks.
Applications of Drag Teaching Robots Welding
Drag teaching robots welding is transforming industries with its versatility:
Construction and Shipbuilding: Ideal for large, irregular welds on structural components.
Custom Fabrication: Supports bespoke metalwork, such as sculptures or architectural features.
SMEs: Enables small businesses to adopt robotic welders without extensive programming expertise.
Prototyping: Facilitates rapid weld path creation for product development.
Traditional robotic welding dominates in:
Automotive Manufacturing: High-speed, repetitive welds for chassis and body panels.
Aerospace: Precision welds for critical components like turbine blades.
Heavy Machinery: Consistent welds for large-scale equipment.
Extended keywords: robotic welding applications, industry-specific weld automation, versatile welding robots.
Benefits of Drag Teaching Robots Welding
Reduced Training Time: Operators learn drag teaching in hours, compared to weeks for traditional programming.
Enhanced Productivity: Quick reprogramming minimizes downtime, boosting throughput.
Accessibility: Democratizes weld automation for businesses with limited technical resources.
Safety: Keeps workers away from hazardous welding zones, aligning with modern safety standards.
Challenges and Considerations
While drag teaching robots welding offers numerous advantages, it’s not without challenges. Manual teaching may introduce slight inconsistencies in high-precision applications. Additionally, for extremely high-volume production, traditional robotic welding remains more efficient. Businesses must evaluate their production needs, weld complexity, and budget when choosing between these automated welding solutions.
Future of Robotic Welding
The future of robotic welding lies in hybrid systems that combine drag teaching’s simplicity with traditional methods’ precision. Advances in AI, machine learning, and sensor technology will further enhance weld automation, enabling robots to self-correct paths and optimize welds in real-time. Keywords like AI-driven robotic welding and smart weld automation are gaining traction as the industry evolves.
Conclusion
Drag teaching robots welding offers a game-changing approach to weld automation, providing flexibility, ease of use, and cost savings compared to traditional robotic welding. While traditional methods excel in high-volume, repetitive tasks, drag teaching empowers SMEs and dynamic industries to adopt robotic welders efficiently. By understanding the strengths of each method, businesses can choose the right automated welding system to optimize their production.