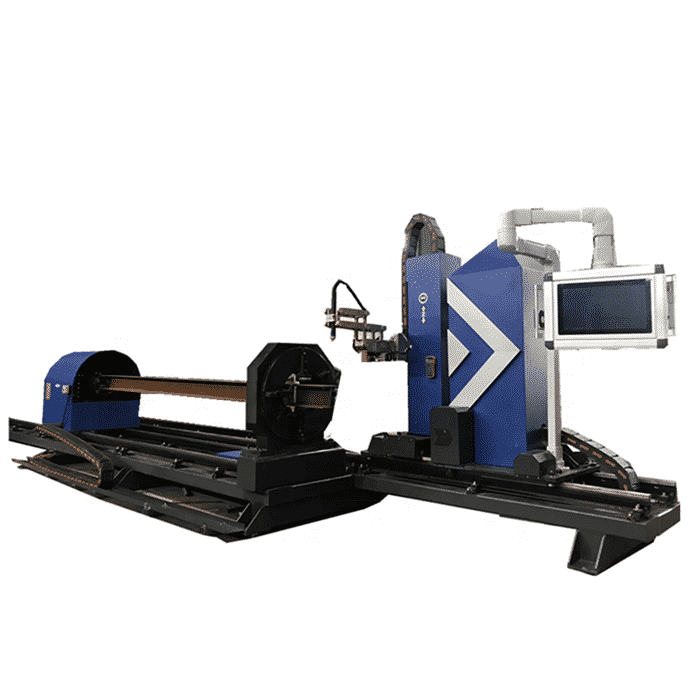
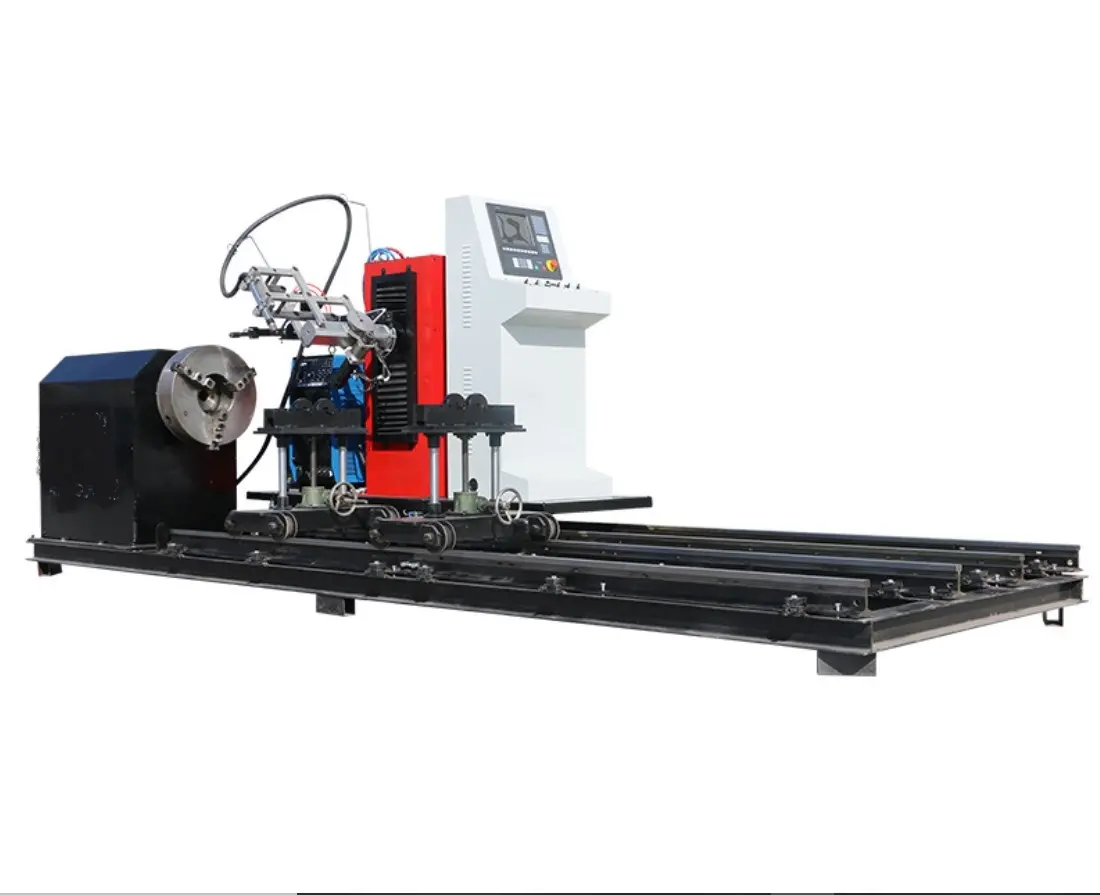
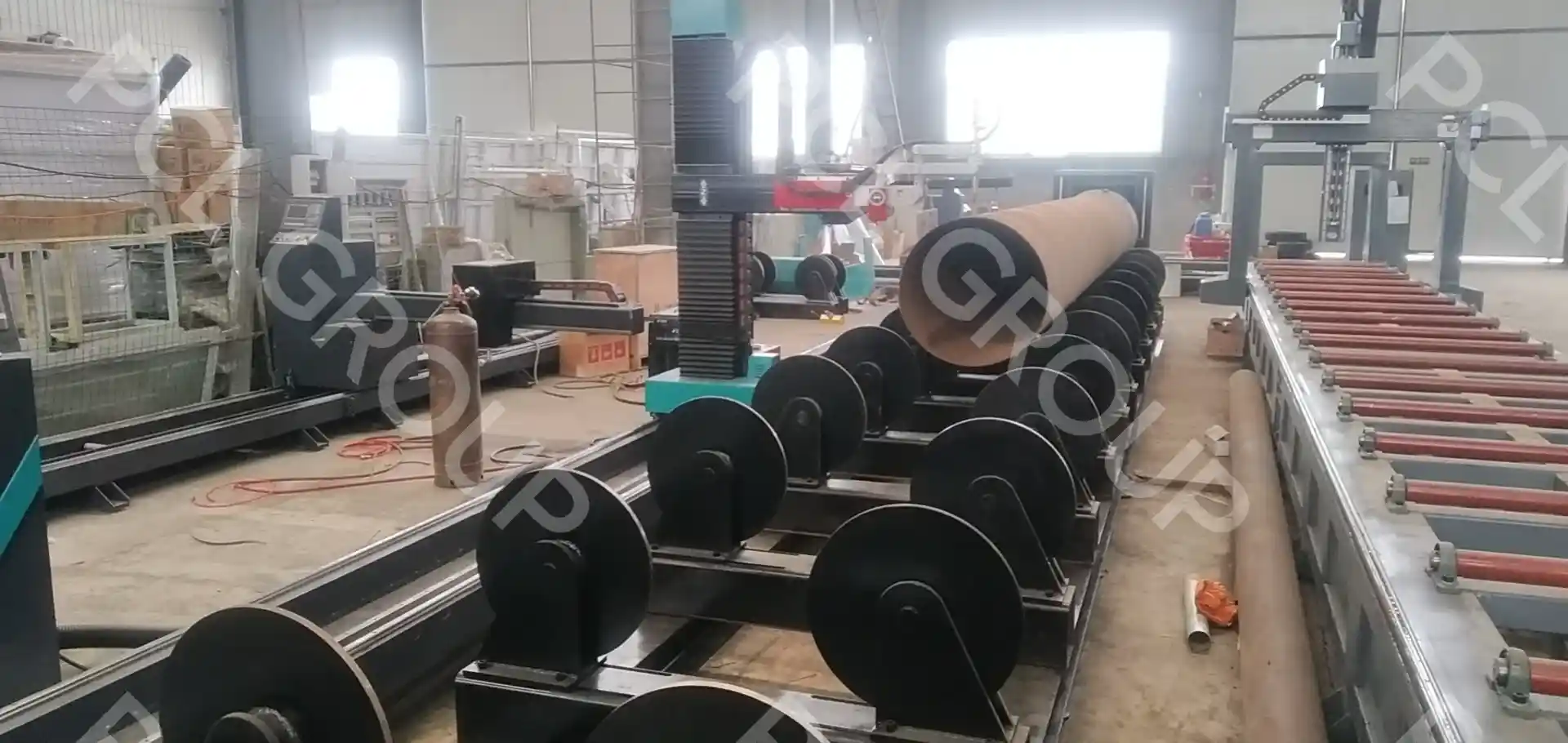
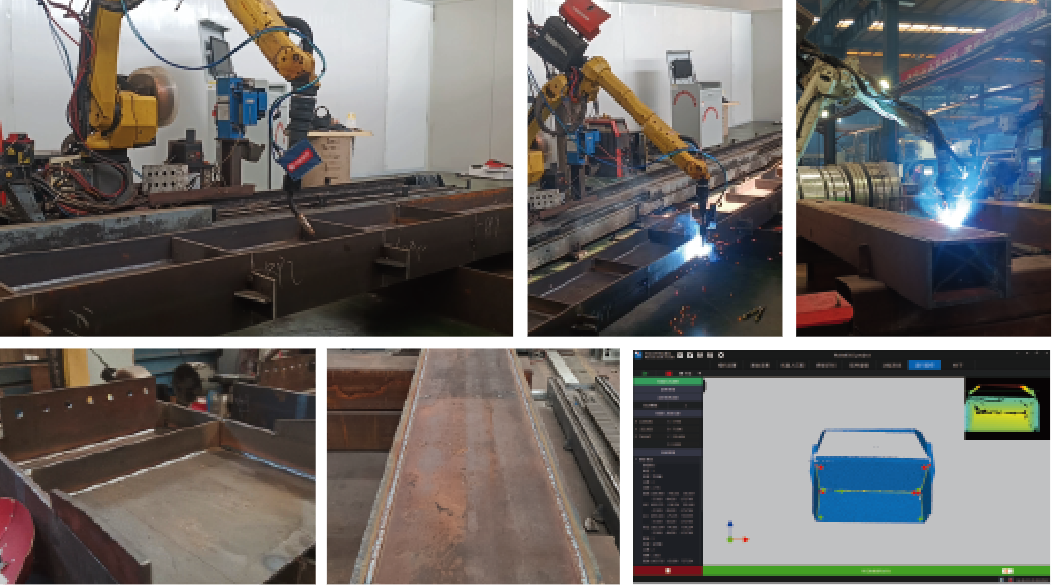
The specific welding speed of a robot depends on the welding task and the material being welded. Generally, the welding speed can range from 20 to 60 cm per minute, depending on the welding speed, welding distance, seam size, and the robot’s matching performance..

Technical Parameters of Robotic Welding:
- Number of Robot Axes: Determines flexibility and is chosen based on workpiece and welding process requirements.
- Load Capacity: Refers to the robot’s ability to handle the weight of the tools and materials.
- Working Radius: Defines the effective working space of the robot.
- Repeatability: Measures the robot’s precision in repeated operations.
- Maximum Speed: The highest operational speed achievable.
- Control System: The core for robot operation and monitoring, such as vector control, digital control, or PLC.
Process Parameters of Robotic Welding
Welding Speed:
- Depending on the specific welding standards and robot type, the welding speed can range from 50 to 160 cm/min.
- For instance, six-axis robots can achieve speeds of 50 to 160 cm/min, while four-axis robots are slower, typically 40 to 90 cm/min.
Factors Affecting Welding Speed:
- Parameters such as welding current, voltage, gas flow rate, as well as the robot’s control system and performance, influence the welding speed. Adjustments are necessary in practical applications to achieve optimal welding results.
Key Parameters of Robotic Welding:
- Robot Type: Six-axis or four-axis robots, with specific control systems.
- Welding Parameters: Current, voltage, gas flow rate, and others.
- Welding Gun Features: Adjustable range, swing function, and sensor interface capabilities.
- Additional Functional Requirements: Swing frequency, swing amplitude, collision detection, etc.
- Repeatability Precision: Accuracy in trajectory repetition.
- Payload Capacity: Includes welding gun, cables, and other accessories.
- Noise Levels: Sound grade and frequency.
- Control Precision: Includes position and speed control accuracy.
- Environmental Conditions: Parameters such as temperature and humidity.
Robotic welding process parameters, such as welding current, voltage, shielding gas flow rate, gun posture, swing frequency, amplitude, and swing type, significantly affect the weld’s shape, width, and depth.
In conclusion, robotic welding parameters should be tailored and optimized based on specific application scenarios and robot types to achieve the best welding performance. These include technical parameters like welding power/current, voltage, speed, distance, and shielding gas specifications, as well as process parameters for electrode trajectory design and dynamic monitoring. Adjustments are made depending on welding tasks and material characteristics