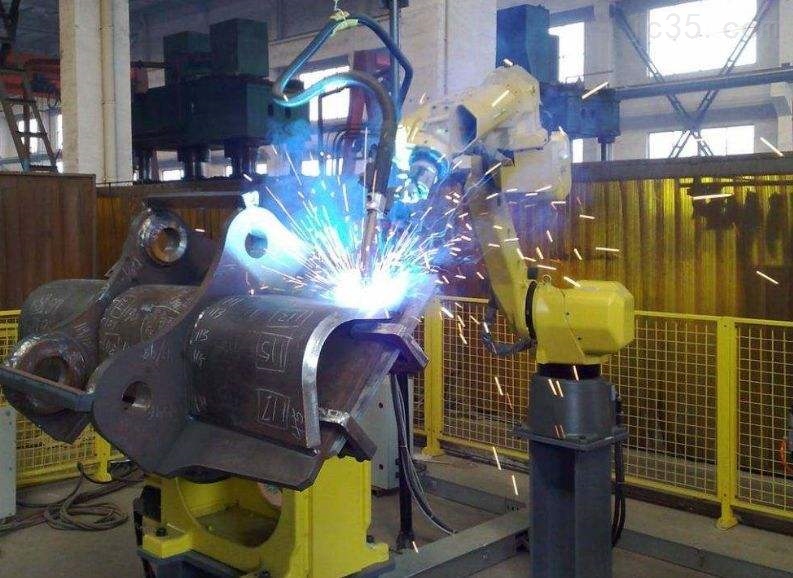
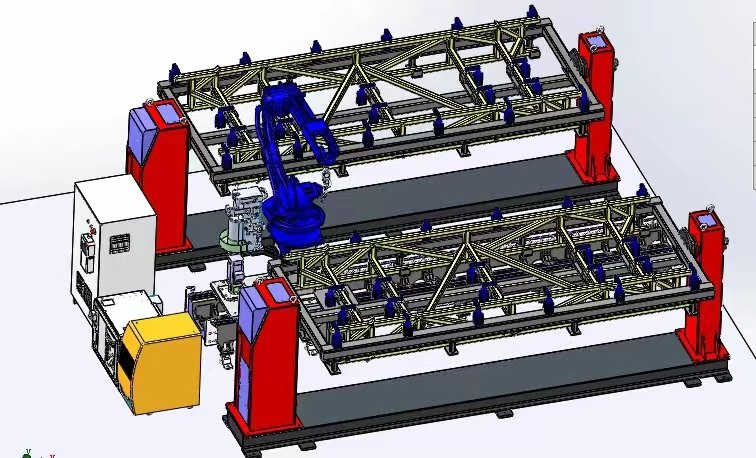
With the continuous development of industrial automation, welding technology has also undergone revolutionary changes. Six-axis welding robots, known for their high precision, efficiency, and stability, have been widely applied across various industries. These robots are automated devices used in industrial production, offering flexible operation and high efficiency. Today, let’s follow along with the welding seam tracking editor from Chuangxiang Zhikong to learn about the operating procedures of six-axis welding robots.

1. Robot Preparation
Power-On Self-Test: Start the robot control system and run the self-test program to ensure the system is functioning normally, with no error messages.
Load Welding Program: Select and load the appropriate welding program into the robot control system based on the shape, material, and welding requirements of the workpiece.
Calibrate Robot Coordinate System: Use a teach pendant or an automatic calibration tool to calibrate the robot’s coordinate system, ensuring the robot can accurately identify the workpiece’s position.
2. Workpiece Clamping and Positioning
Workpiece Clamping: Secure the workpiece to be welded on the welding workbench, ensuring it is stable and accurately positioned.
Workpiece Positioning: Use a vision system or laser sensors to precisely position the workpiece, providing accurate coordinate information for the subsequent welding operations.
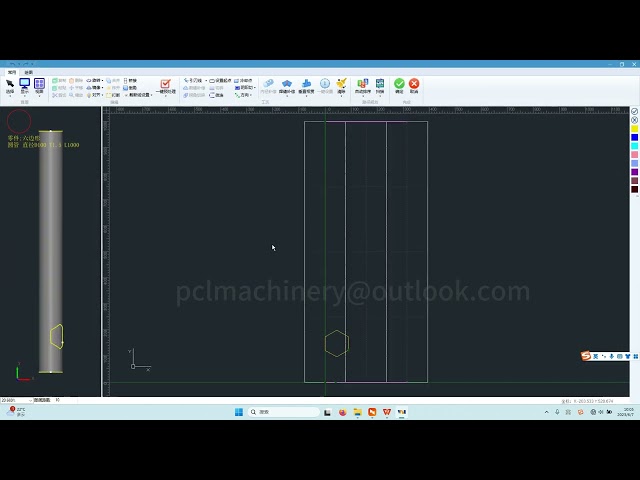
3. Teaching and Programming
Teaching Mode: Switch the robot to teaching mode, manually operating the robot with the teach pendant to teach the welding trajectory.
Recording the Trajectory: During the teaching process, the robot will record information in real-time, including the coordinates, speed, and acceleration of the welding trajectory.
Generate Welding Program: After completing the teaching process, the robot will generate the corresponding welding program based on the recorded trajectory information.
4. Automatic Welding
Start Automatic Welding: Switch the robot to automatic welding mode and start the generated welding program.
Real-Time Monitoring: During automatic welding, the welding status can be monitored in real-time through the teach pendant or monitoring software to ensure welding quality.
Adjust Parameters: Adjust welding parameters such as current, voltage, and speed as needed, based on the real-time monitoring of the welding status, to achieve optimal welding results.
5. Finishing Work
Turn off the robot’s power. Clean the welding area. Inspect the welding quality of the workpiece and make any necessary repairs.
6. Precautions
When operating a six-axis welding robot, the following precautions should be observed:
Strictly adhere to safety operation procedures and wear the necessary protective gear.
Do not perform maintenance or repairs while the robot is in operation.
If any abnormalities are detected, stop the operation immediately and troubleshoot the issue.
Operating a six-axis welding robot is relatively complex and requires professional training before one can be qualified to operate it. As technology continues to develop, six-axis welding robots will see even broader applications, providing more efficient solutions for automated manufacturing processes.
Precision Engineering Solutions
Transform Your Production with Cutting-Edge Laser Welding
Unleash unparalleled welding excellence with PCL Group’s innovative robot laser welding machines. Elevate your production efficiency with precision technology tailored for your industry.
- Cutting-edge laser precision.
- Seamless robotic integration.
- Tailored welding settings.