Overview of Laser Technology in the Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, laser technology is primarily used for body assembly, welding, and component welding. Laser tailored blank welding is employed during car body design and manufacturing, where steel plates of various specifications are selected and processed through laser cutting and assembly to meet specific design and performance requirements for different body parts. Over the past decade, laser welding has evolved from being used only for roof connections to being applied extensively throughout the entire car body.
1. Advantages of Laser Welding
Laser tailored blank welding offers numerous benefits, including reducing the number of components and molds, minimizing spot welds, optimizing material usage, decreasing part weight, reducing costs, and improving dimensional accuracy. Laser welding is mainly used for body frame structures, such as welding the roof to the side body. Traditional resistance spot welding methods have gradually been replaced by laser welding.
By employing laser welding, the joint interface width between workpieces can be reduced, which decreases material usage while increasing the vehicle’s rigidity. Currently, this technology has been adopted by leading manufacturers of high-end cars and major parts suppliers worldwide.
2. Process Characteristics of Laser Welding
Laser welding can be categorized into two basic modes based on the mechanism of weld pool formation: heat conduction welding and deep penetration welding.
Heat Conduction Welding:
This mode uses a lower laser power density (10⁵–10⁶ W/cm²). The laser energy is absorbed by the workpiece, causing surface melting, and heat is conducted internally to form a molten pool. This mode results in shallow penetration and a low depth-to-width ratio.
Deep Penetration Welding:
This mode involves a higher laser power density (10⁶–10⁷ W/cm²). The absorbed laser energy rapidly melts and even vaporizes the metal. The vaporized metal forms a small hole under the pressure of the vapor. The laser beam can reach the bottom of this hole, allowing it to extend further until a balance is achieved between vapor pressure, surface tension of the molten metal, and gravity. The molten metal flows around the small hole as the laser beam moves along the welding direction, solidifying into a weld seam. This mode provides greater penetration and a high depth-to-width ratio, making it the standard choice in the automotive industry
During deep penetration welding, metal vapor and shielding gases ionize under the laser’s action, forming plasma inside and above the keyhole. Plasma can absorb, refract, or scatter the laser, potentially weakening the laser energy reaching the workpiece. Non-reactive side-blow gases like helium or argon are often used to mitigate this issue.
3. Laser Welding Equipment
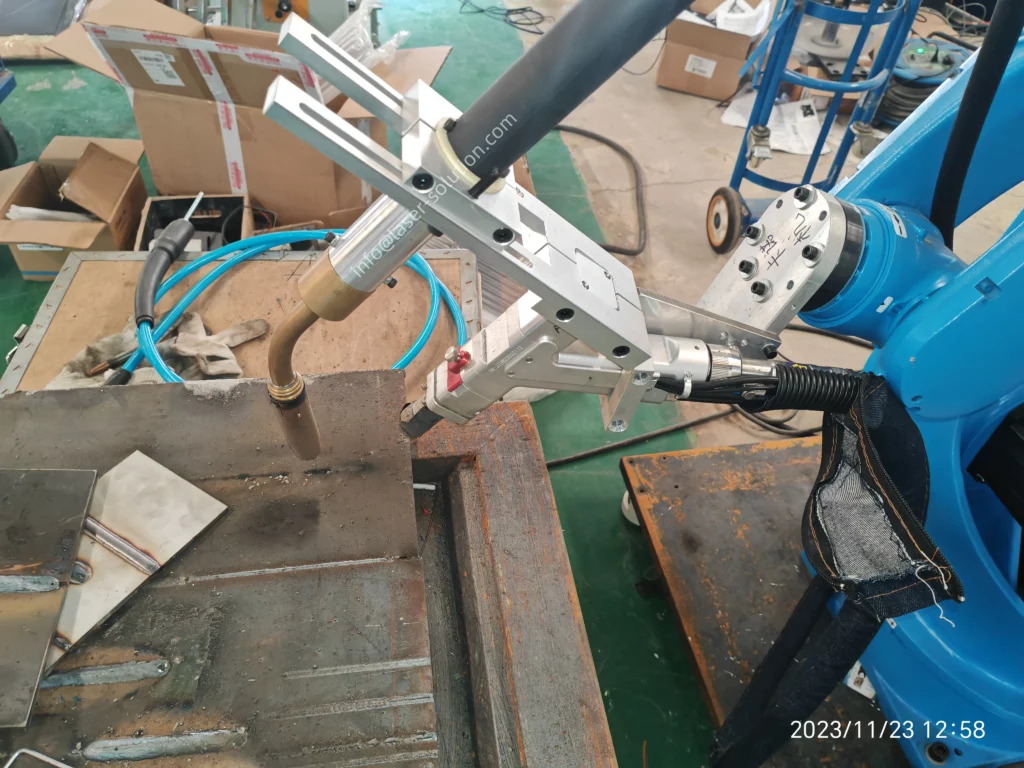

Laser welding equipment typically comprises:
Laser Welding Chamber:
To protect operators, a fully enclosed chamber is designed to meet FDA Class 4 laser safety standards.
Laser Generators:
Common types include CO₂ lasers and YAG solid-state lasers. CO₂ lasers are preferred for high-power applications, while YAG lasers, with advancements in recent years, are increasingly used for specific applications due to their ability to transmit via optical fibers.
Optical Delivery and Focusing Systems:
These systems include components like beam expanders, mirrors, and lenses that focus and direct the laser beam.
Laser Welding Machines:
These enable relative motion between the laser beam and workpieces, utilizing CNC systems or robotic arms for precision.
4. Development and Innovations in Laser Welding
New advancements are expanding the application scope and control level of laser welding:
Filler Wire Laser Welding:
Reduces assembly gap requirements by filling the joint with a metal wire, enabling better weld formation even with larger gaps.
Beam Oscillation Welding:
Rotating the laser beam during welding allows for greater tolerance in joint alignment and gap.
Online Monitoring and Quality Control:
Real-time monitoring of plasma signals (optical, acoustic, and charge-based) facilitates automatic feedback control of the welding process
Current State of Laser Welding in Automotive Manufacturing
Laser welding has become a mature and widely adopted technology in automotive manufacturing. Companies like Volkswagen, BMW, and Mercedes-Benz extensively utilize it for tasks such as roof welding and transmission components. The technology significantly enhances vehicle safety, weight reduction, and structural precision, marking a key trend in the industry.