Introduction
In the field of sheet metal processing, laser cutting machines have demonstrated significant advantages. Due to their high precision, fast speed, and excellent quality, they have gradually replaced traditional processing methods and have become the core equipment for sheet metal cutting [1]. From the emergence of laser cutting machines to the replacement of YAG and CO2 machines by fiber laser cutting machines, and now with the continuous launch of high-power laser cutting machines, high-power equipment has become the main trend for thick plate cutting and efficiency improvement.
In recent years, high-power laser cutting machines have become a hot topic in the field of laser cutting. Many companies have introduced fiber laser cutting equipment with power levels exceeding 10,000W. For the sheet metal processing industry, the emergence of high-power cutting equipment has significantly increased both the thickness and efficiency of sheet metal cutting. These machines continuously push the limits of material cutting thickness, reduce the cost of thick plate processing, and create a positive cycle that further expands the application field of laser cutting.
Introduction to High-Power Laser Cutting Machines
(1) Overview of High-Power Cutting Machines
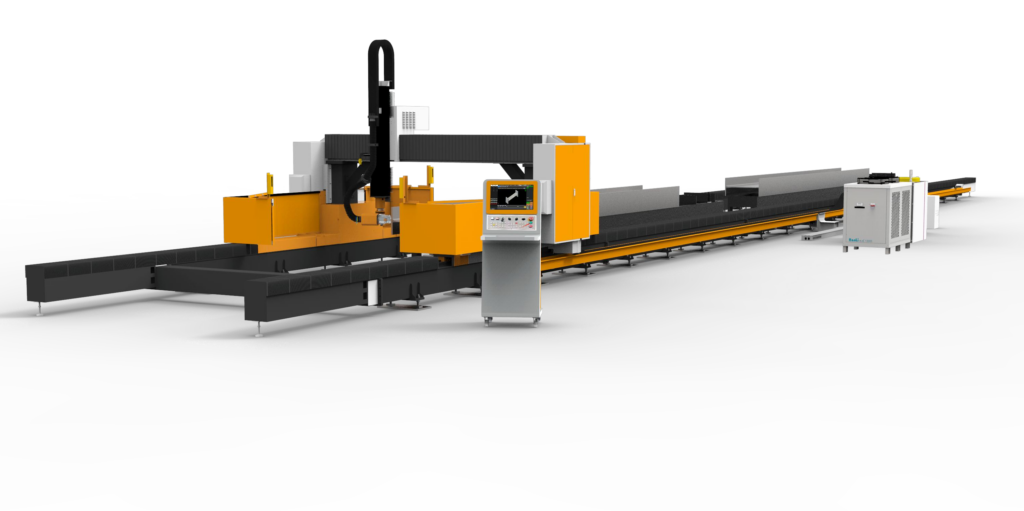
Laser cutting machines can be classified by power into low-power, medium-power, and high-power machines. For moderate-thickness stainless steel and carbon steel, low-power laser cutting machines can achieve good cutting results. However, for thick plate cutting and efficiency improvement, high-power laser cutting machines are more suitable. Therefore, laser cutting machines with power levels exceeding 10,000W are collectively referred to as high-power laser cutting machines (see Figure 1).
(2) Power Specifications of Fiber Lasers
To accommodate different sheet metal thicknesses, the power specifications of fiber lasers used in high-power cutting machines vary. According to current trends, companies in the metal processing market are gradually upgrading to various power levels, as shown in Table 1.
| Power Level (kW) | 10 | 12 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Note | Common | Common | Common | Rare | Rare | Rare | Rare |
(3) Gas Usage Specifications
To ensure cutting accuracy, speed, and smooth cutting surfaces, high-power laser cutting machines require high-purity oxygen, typically with a purity level of 99.99%.
### Features of High-Power Laser Cutting Machines
3.1 Technological Advancements
(1) High-Dynamic Performance of High-Speed Cutting Machines
Machines equipped with 10,000W-class fiber lasers adopt a new triangular beam structure with the following features:
- Weight is reduced by 30%, significantly improving dynamic performance.
- Maximum movement speed reaches 200m/min with an acceleration of 4g.
- The base weight is increased by approximately 20% to enhance stability and eliminate the impact of high-acceleration movements.
(2) New Software System
The software and control system function as the brain and command center of the machine. In addition to hardware upgrades, differences in machine performance mainly stem from variations in software and control systems, which can be substantial.
(3) Stable Cutting at 100m/min
- The capacitive sensor’s response speed is three times faster than that of traditional cutting heads.
- The Z-axis speed is increased, enabling continuous and uninterrupted operation, improving thin plate cutting efficiency by more than 30%.
- Enhanced piercing and precision drilling functions, along with remote diagnostics, meet the requirements of Industry 4.0 [2].
3.2 Cutting Head Features
The high-power cutting head is a crucial component that ensures stable cutting during continuous high-power operation, offering:
- Better sealing, improved cooling, a wider focus range, and high-temperature-resistant lenses.
- A newly designed gas circuit and nozzle structure to counteract focal point displacement caused by prolonged operation, improving cutting speed and stability.
3.3 High-Power Cutting Capability
(1) Increased Cutting Thickness
Currently, high-power laser cutting machines can cut aluminum alloy sheets up to 40mm thick and stainless steel sheets up to 130mm thick. With ongoing technological advancements, cutting thickness capabilities will continue to increase, reducing processing costs and accelerating the adoption of high-power laser cutting for thick plate applications [3].
(2) Increased Efficiency for Thin and Medium Plates
- When cutting stainless steel sheets between 3 and 10mm thick, a 10,000W laser cutter is more than twice as fast as a 6,000W cutter.
- In carbon steel applications, a 10,000W laser cutter can achieve a bright surface cutting speed of 18-20mm/s, double the standard cutting speed.
- Compressed air or nitrogen can be used to cut carbon steel sheets up to 12mm thick, with an efficiency 6 to 7 times greater than oxygen cutting.
3.4 Machine Bed Features
(1) High Load-Bearing Mechanical Structure
High-power cutting machines are equipped with cast iron beds, integrally cast using graphite iron with a minimum tensile strength of 200 MPa. This significantly enhances carbon content, compressive strength, vibration damping, and wear resistance (see Figure 3).
(2) Advantages of Cast Iron Beds
- Excellent lubrication, corrosion resistance, and dimensional stability, reducing processing errors caused by machine bed vibrations.
- Less wear during operation, improving stability by over 30%, accuracy by over 30%, and extending the machine bed’s lifespan to over 70 years.
3.5 Automatic Nozzle Replacement
(1) Manual Nozzle Replacement
Traditionally, nozzles are manually replaced based on material thickness and type, leading to inefficiencies and inconsistent precision.
(2) Automatic Nozzle Replacement Technology
Modern high-power laser cutting machines feature automatic nozzle replacement, calibration, and cleaning, reducing labor intensity and improving accuracy. Key benefits include:
- Reduced manual workload and improved positioning accuracy.
- Automatic nozzle selection based on material and thickness, minimizing downtime and increasing production efficiency.
- A closed protection system that enhances equipment and personnel safety.
3.6 Rapid Piercing and Extremely Small Hole Formation
(1) Rapid Piercing
- Reduces piercing time by 90%, minimizes thermal focus, and stabilizes cutting. Table 2 illustrates its benefits.
(2) Extremely Small Hole Cutting
Traditional laser cutting assumes that the minimum hole diameter is equal to the sheet thickness. However, high-power machines can cut holes as small as 0.15 times the sheet thickness or even smaller (see Figure 4).
Advantages of High-Power Laser Cutting Machines
High Speed:
Cutting speeds exceed 20m/min, with axis movement speeds reaching up to 250m/min and acceleration of up to 10g.
High Precision:
Capable of cutting approximately 500 holes of ϕ10mm per minute in 1mm thick sheets with minimal error.
Thick Plate Processing:
The continuous increase in power levels allows for the cutting of thicker plates.
Large-Scale Cutting:
The processing range continues to expand to accommodate larger sizes.
Automation and Intelligence:
Integration with Industry 4.0, remote control, automated nesting, and intelligent diagnostics.
Conclusion
Development of High-Power Equipment:
High-power laser cutting represents the future of metal processing, with ongoing research focused on speed, precision, large-scale cutting, 3D applications, and special materials.
Equipment Selection:
Companies must carefully evaluate stability, consistency, speed adjustment, control system advancements, and machine lifespan when selecting high-power laser cutters. Unlike low-power machines, price should not be the decisive factor, as high-power machines involve significant investment and risk.